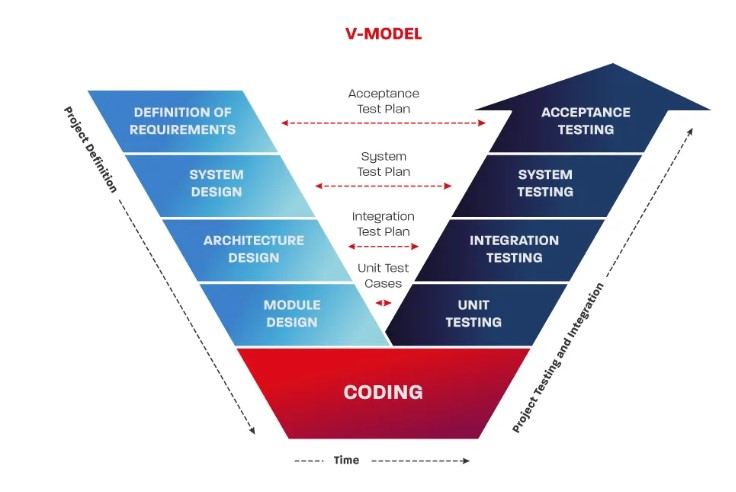
The V-Model is an improved version of the classic Waterfall Model. In this model, each stage includes a control mechanism to ensure that it is ready before moving on to the next level. Testing begins as early as the requirements phase, and each subsequent development phase has a corresponding level of test coverage planned.
History of the V-Model
The concept of the V-Model was developed independently by Germany and the United States in the late 1980s:
- The German V-Model was developed by the aerospace company IABG in Ottobrunn, near Munich, in cooperation with the Federal Office of Defense Procurement in Koblenz, for the German Ministry of Defense. The model was officially adopted in 1992.
- The American V-Model (VEE) was developed by the National Council on Systems Engineering (international since 1995) for satellite systems, including hardware, software, and user interaction.
The modern version of the V-Model is called V-Model XT, which was officially introduced in February 2005.
The V-Model is used for managing the software development process within the German federal administration. Today, it is a standard for German government and defense projects, as well as for software developers in Germany.
The V-Model serves more as a set of standards for projects involving the development of new products. It is largely similar to PRINCE2 and describes methods for both project management and system development.
Main Stages of the V-Model
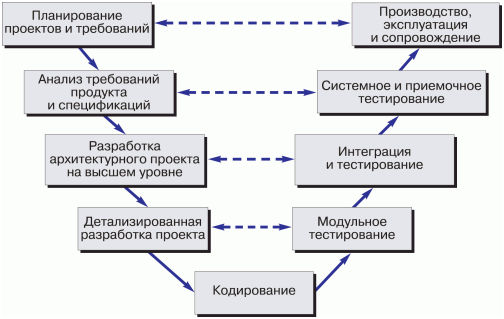
Project and Requirements Planning – At this stage, system requirements are defined, and resources are allocated to ensure alignment with the defined goals.
Product Requirements Analysis and Specification – Existing requirements are analyzed, resulting in a complete specification of the software system.
High-Level Architectural Design – Defines how the software functions will be implemented during the project execution.
Detailed Design – Algorithms for each task outlined in the architectural design phase are defined and documented.
Code Development (Implementation) – Algorithms from the detailed design phase are transformed into working software code.
Module Testing (Unit Testing) – Each software module is tested individually to identify errors.
Integration and Testing – Previously tested individual modules are integrated and tested as a group to confirm that they function correctly together.
System and Acceptance Testing – The complete software system is tested in the hardware environment defined in the requirements specification to ensure it functions as intended.
Deployment, Operation, and Maintenance – The software is deployed for use, and updates or fixes are made as needed during its lifecycle.
Acceptance Testing – The system’s functionality is tested to ensure it meets the original requirements.
Advantages of the V-Model:
✅ Advantages of the V-Model
The V-Model is an evolution of the Waterfall Model and therefore inherits all of its strengths:
- Early planning of system development and testing stages.
- Verification and validation of all intermediate development results.
- Easier tracking of the development process compared to the Waterfall Model, with a more realistic use of the project timeline.
- Simplicity of use – the model is straightforward to understand and implement.
❌ Disadvantages of the V-Model (when applied to an unsuitable project):
- Difficulty in supporting parallel activities – the model is linear and not designed for overlapping phases.
- No built-in iteration between phases – which limits flexibility if something needs to be revisited.
- Inability to introduce dynamic changes to requirements at different stages of the lifecycle.
- Late testing of requirements – if requirements need to change after testing, it can greatly impact the project timeline.
- Lack of risk analysis – the model does not include steps specifically aimed at identifying and mitigating risks.
Scope of Application of the V-Model
The use of the V-Model is most effective in the following cases:
- When developing projects with clearly defined and well-documented requirements that are available in advance.
- When working on projects where the implementation methods and technologies are known and understood, and the development team has prior experience with them.
- When developing systems that require high reliability, such as in defense, aerospace, medical, or critical infrastructure applications.
Sources
- https://qalight.ua/ru/baza-znaniy/v-model-v-model-2/
- https://studfile.net/preview/1444530/page:5/
- https://habr.com/ru/articles/111674/
- https://www.gpntb.ru/win/inter-events/crimea2009/disk/138.pdf
- https://ru.wikipedia.org/wiki/V-Model
- https://qarocks.ru/v-model/
- https://chatgpt.com/share/672b46fc-c54c-8004-a07c-fa1a1a9961c5

